An overview of New GST Registration
GST, short for Goods and Services Tax, is an indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services in India. Introduced in 2017 as a significant reform, GST replaced multiple central and state taxes and cesses to streamline the taxation system. Its primary objectives are to simplify tax compliance, eliminate the cascading effect of taxes, broaden the tax base, and enhance overall compliance.
GST operates on the principle of destination-based taxation, meaning the tax is collected by the state where the goods or services are consumed rather than where they are produced or supplied. It is also a value-added tax, imposed only on the value added at each stage of the supply chain, rather than the entire transaction value.
Additionally, GST registration is mandatory for certain individuals under the reverse charge mechanism. This includes importers, recipients of services from unregistered suppliers, or agents acting on behalf of suppliers. The online GST registration process facilitates compliance for such entities.
What Is GST Registration?
GST registration is the process by which a business entity obtains a unique identification number from the government, making it eligible to pay Goods and Services Tax (GST) on the supply of goods or services. It is mandatory for specific categories of businesses, including those with an annual turnover exceeding ₹40 lakhs, entities engaged in inter-state trade, e-commerce operators, non-resident taxable persons, and others. Registering for GST online offers businesses several advantages under the GST framework. These include eligibility to claim input tax credit, ensuring a seamless flow of credit across the supply chain, and enhancing their compliance rating. Additionally, new GST registration promotes transparency, accountability, and the prevention of tax evasion in the system.
What is GSTIN (Goods and Services Tax Indication Number)?
GSTIN, or Goods and Services Tax Identification Number, is a unique 15-digit alphanumeric code assigned to every registered taxpayer under India’s GST system. This number contains critical details, including the state code, the taxpayer’s PAN (Permanent Account Number), the registration number, the entity code, and a checksum digit. GSTIN plays a vital role in tracking the tax liability and compliance of registered taxpayers. It also streamlines processes like filing GST returns and making tax payments online, ensuring efficiency and transparency within the GST framework.
Mandatory Documents for GST Registration:
To apply for GST registration online, a business entity must submit specific mandatory documents along with the application form. While the required documents may vary based on the type and nature of the business, some common documents required for all entities include:
Partnership deed or LLP agreement for partnership firms or LLPs
Certificate of incorporation, memorandum of association and articles of association for companies
Letter of authorization or board resolution for authorized signatory
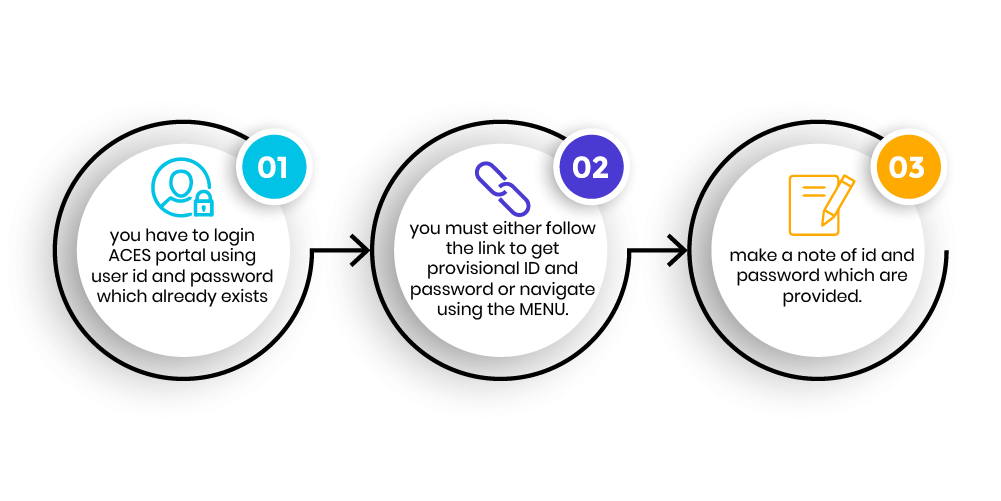
GSTIN or provisional ID of the existing taxpayers under the previous tax regime
Proof of major place of business and a second location
Details and proof of constitution of business (such as trust deed, society bye-laws, etc.)
Depending on the type of entity, some additional documents may be required, such as:
PAN card of the business entity or the applicant (proprietor, partner, director, etc.)
Aadhaar card of the applicant
Proof of business address (such as electricity bill, rent agreement, property tax receipt, etc.)
Bank account details (such as cancelled cheque, bank statement, passbook, etc.)
Digital signature or E-signature of the applicant
Valid email address and mobile number for verification and communication
Applicants must ensure that all required documents are scanned and uploaded in either PDF or JPEG format, adhering to a maximum file size of 1 MB. Additionally, all information provided in the application form must be accurate and complete, as any errors or discrepancies could result in delays or rejection of the application. After submitting the application, an acknowledgment number is generated. This number allows the applicant to track the status of their GST registration online, ensuring transparency and ease throughout the process.
Who Should Apply For New GST Registration Online?
GST Registration Online is mandatory for certain categories of taxpayers, such as:
Businesses or individuals supplying goods or services in India are required to register under GST if their annual turnover exceeds ₹40 lakhs in a financial year (₹10 lakhs for special category states).
Businesses or individuals engaged in inter-state trade or commerce of goods or services are required to register under GST, regardless of their annual turnover.
Businesses or individuals liable to pay tax under the reverse charge mechanism are mandatorily required to register under GST, irrespective of their turnover.
Businesses or individuals acting as agents or intermediaries on behalf of suppliers or recipients of goods or services are required to register under GST, regardless of their turnover.
Businesses or individuals operating as e-commerce operators or aggregators are mandatorily required to register under GST, irrespective of their annual turnover.
Businesses or individuals who are required to deduct tax at source (TDS) or collect tax at source (TCS) under GST are also obligated to register under the GST system, regardless of their turnover.
Businesses or individuals engaged in supplying online information and database access or retrieval (OIDAR) services to non-taxable online recipients are required to register under GST, regardless of their turnover.
Businesses or individuals who are non-resident taxable persons or casual taxable persons must register under GST, irrespective of their turnover.
New GST Registration Process in India
Identify the specific type of GST registration that applies to your business.
Gather all necessary documents and information required for the GST registration process.
Access the GST Online Registration portal and complete the application form.
Authenticate your details using Aadhaar verification or Electronic Verification Code (EVC).
Submit the application to receive an acknowledgment number.
Await the approval of your GST registration and the issuance of your GSTIN.
Online GST Registration Process for New Business
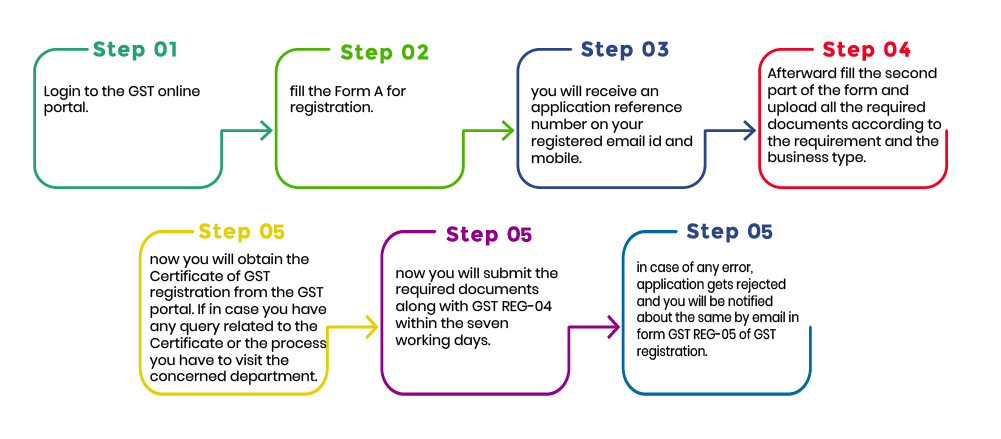
Go to the official GST portal and navigate to Services > Registration > New Registration.
Choose the Taxpayer category (e.g., Regular, Composition, Casual Taxable Person) and provide details such as legal name, PAN, email address, and mobile number.
Log in using the TRN and complete the application form by entering details such as business address, bank account information, authorized signatory, and other required information.
Upload the necessary documents, such as proof of identity, proof of address, photographs, and other documents, based on the type of business entity.
Submit the application using a digital signature certificate (DSC) or an Aadhaar-based electronic verification code (EVC).
Receive the Application Reference Number (ARN) on your registered email and mobile number, and use it to track the status of your application on the GST portal.
Once the application is approved, download the GST registration certificate from the portal.
Types Of GST Registration Online:
There are primarily two types of GST Registration Online that can be done online:
- Regular GST Registration: Most businesses required to register under GST must undergo regular GST registration. This registration is suitable for businesses that provide goods or services either within a single state or across multiple states in India. Below are the key steps involved in the regular GST registration process:
a. Navigate to the GST Online Portal: The applicant must visit the official government GST portal.
b. Complete the Online GST Registration Application Form: The applicant needs to provide relevant details such as the legal name of the business, address, PAN (Permanent Account Number), bank account information, and contact details. Required documents may include the business owner’s PAN card, identity proof, address proof, and proof of business registration.
c. Submit the Application and Receive the Application Reference Number (ARN): After completing and submitting the application form, an Application Reference Number (ARN) will be generated. This number helps in tracking the application’s status.
d. Verification and Processing: The GST authorities will verify the provided information and documents. Once the verification is complete and accurate, the GST registration will be approved, and the business will receive a GSTIN (GST Identification Number).
2. Regular GST Registration: Most businesses required to register under GST must undergo regular GST registration. This registration is suitable for businesses that provide goods or services either within a single state or across multiple states in India. Below are the key steps involved in the regular GST registration process:
a. Log in to the GST Portal: The applicant needs to log in to the official GST portal, similar to the standard GST registration process.
b. Complete the Composition Scheme Application: The applicant must provide essential information, including the legal name of the business, address, PAN, bank account details, and contact information. Documents verifying the business owner’s identity and address may also be required.
c. Submit the Application and Receive the Application Reference Number (ARN): After submitting the application form, an Application Reference Number (ARN) will be generated, allowing the applicant to track the status of the application.
d. Verification and Processing: Once the application is verified, and everything is in order, the Composition Scheme registration will be approved. The business will receive a GSTIN and gain eligibility for the benefits of the Composition Scheme.
Benefits Of Online GST Registration:
Benefits of Online GST Registration: There are several advantages to registering for Goods and Services Tax (GST) online. Below are some key benefits:
- Convenience: Online GST registration allows you to apply from anywhere and at any time, as long as you have an internet connection. You don’t need to visit a physical office or wait in long queues, saving you both time and effort.
- Timesaving: The online registration process is typically faster than the traditional offline method. You can complete and submit your application and documents electronically, which speeds up the process.
- Paperwork Reduction: Online GST registration significantly reduces paperwork. You can upload documents digitally rather than handling physical copies, making it easier to organize and store your records.
- Real-time Status Updates: With online registration, you can track the progress of your application in real time. You’ll receive updates at every stage, such as submission, verification, and approval.
- Transparency: The online process is transparent, as all information and documents are submitted electronically. This reduces the chances of errors or inconsistencies and promotes accountability.
- Access to Information: Online registration portals often provide access to various resources related to GST compliance. FAQs, user manuals, and other educational materials help you better understand the GST rules and regulations.
- Integration with Other Systems: Online GST registration can be integrated with other government systems, such as tax filing platforms. This integration helps streamline your compliance processes and reduces the chances of data entry errors.
- Simple Amendments and Updates: If you need to make changes to your GST registration details, the online portal allows you to easily update information like your business profile, address, or contact details.
- Remote Area Accessibility: Online registration ensures that businesses in remote or rural areas have the same access to GST registration as those in urban locations. It eliminates the need for physical presence, making the process more inclusive.
- Cost-effective: Online GST registration is often more cost-effective compared to the offline process. It eliminates travel expenses, reduces paperwork, and simplifies the registration process, potentially saving money.
GST registration is the process through which a business or individual becomes recognized as a taxpayer under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system in India. It involves obtaining a unique GST Identification Number (GSTIN) from the government. GST registration is mandatory for businesses that meet specific criteria, such as exceeding a certain turnover threshold, engaging in inter-state trade, or providing certain types of services. Once registered, businesses must comply with GST laws, including collecting GST on taxable supplies, filing returns, and maintaining records. It also enables businesses to avail of benefits like input tax credits and easier compliance.
A non-resident taxable person is an individual or business that does not have a permanent establishment in India but is engaged in the supply of goods or services in the country. This category includes foreign businesses or individuals providing taxable supplies in India but not residing or having a fixed place of business there.
A casual taxable person refers to a business or individual who occasionally undertakes taxable supply in India, but does not have a fixed place of business in the country. This could include individuals or companies that participate in temporary activities such as exhibitions, trade shows, or events. Casual taxable persons are required to obtain GST registration for the duration of their activities in India.
Both non-resident and casual taxable persons must apply for GST registration and comply with GST regulations when conducting business in India.
GST registration is generally free of cost. The process of registering for GST through the official GST portal does not require any payment for registration. However, there may be additional costs associated with the following:
- Professional Fees: If you hire a GST consultant, accountant, or a tax professional to help with the registration process, their service fees will apply.
- Documentary Costs: In case you need to obtain certain documents or notarize copies for submission, there may be minor charges.
- GST Compliance: After registration, there might be costs for ongoing compliance, such as fees for filing GST returns, maintaining records, and accounting services, depending on the complexity of your business operations.
In general, the registration itself is a straightforward, free process when done online via the official portal.
To register for New GST Registration Online, follow these steps:
- Visit the GST Portal: Go to the official GST registration portal at www.gst.gov.in.
- Select ‘Services’ and ‘Registration’: On the homepage, navigate to Services > Registration > New Registration.
- Fill in the Application Form:
- Select the Taxpayer Type: Choose the appropriate category (e.g., Regular, Composition, Casual Taxable Person, etc.).
- Provide Details: Enter details like the legal name of the business, PAN (Permanent Account Number), email, mobile number, business address, and bank account details.
- Upload Documents: Upload the necessary documents (PAN card, identity proof, address proof, photographs, etc.) based on your business type.
- Verify Your Details:
- Verify the information provided using Aadhaar authentication or an Electronic Verification Code (EVC).
- Submit the Application: After filling in all the details, submit the form. Upon successful submission, an Application Reference Number (ARN) will be generated.
- Track Application Status: You can track the status of your application using the ARN on the GST portal.
- Approval and GSTIN Issuance: After verification, the GST authorities will approve your application, and you will receive your GSTIN (Goods and Services Tax Identification Number).
- Download the GST Registration Certificate: Once your GST registration is approved, you can download the GST registration certificate from the portal.
By completing these steps, your business will be successfully registered under GST and be able to comply with tax requirements.
The validity of a GST registration number (GSTIN) is typically perpetual, meaning it remains valid as long as the business continues to operate and complies with the GST regulations. However, there are certain circumstances where the GST registration may become invalid or need to be updated:
- Suspension or Cancellation: If the business fails to comply with GST filing or tax payment obligations, the GST registration may be suspended or canceled by the GST authorities.
- Business Closure: If the business is closed or discontinued, the GST registration will be canceled. The business must apply for de-registration on the GST portal.
- Change in Business Details: If there is any change in the business details (e.g., legal name, address, or business structure), the GSTIN may need to be updated to reflect these changes.
- Voluntary De-registration: A business can apply for voluntary de-registration if it no longer meets the requirements for GST registration, such as falling below the turnover threshold for mandatory registration.
In general, as long as the business is operational and complies with all GST requirements, the GSTIN remains valid.
To cancel GST registration, follow these steps:
- Log in to the GST Portal: Visit the official GST portal at www.gst.gov.in and log in using your credentials.
- Navigate to ‘Services’ > ‘Registration’ > ‘Application for Cancellation of Registration’: After logging in, go to Services > Registration and select Application for Cancellation of Registration.
- Fill in the Cancellation Form:
- Provide details such as the reason for cancellation (e.g., business closure, change in business structure, etc.).
- Update any relevant business information, if required.
- Ensure all details are accurate and complete before proceeding.
- Submit the Application: Once the cancellation form is filled, submit it online. After submission, the system will generate an Application Reference Number (ARN) that can be used to track the status of your cancellation application.
- Verification and Processing: The GST authorities will verify your cancellation application. If everything is in order, your GST registration will be canceled.
- Cancel GSTIN: Once approved, your GSTIN will be canceled, and you will receive a confirmation from the GST portal.
Reasons for Cancelling GST Registration:
- Business closure or discontinuation of business activity.
- Sale or transfer of business.
- Voluntary cancellation if the business no longer meets the eligibility for GST registration (e.g., turnover falling below the threshold).
After cancellation, ensure that all pending returns are filed, and taxes are paid to avoid any penalties or interest charges.
The documents required for GST registration depend on the type of business entity, but some common documents are needed for all types of businesses. Here’s a list of documents generally required for GST registration:
1. Proof of Identity:
- For Individuals/Proprietors: PAN card, Aadhar card, or passport.
For Directors/Partners/Authorized Signatories: PAN card and government-issued identity proof (Aadhar card, passport, voter ID, etc.).
2. Proof of Address:
- For Business Place:
- Rent agreement or lease deed (if the business operates from rented property).
- Property tax receipt, electricity bill, or a similar utility bill as proof of address.
- For Residence:
- Utility bill (electricity bill, water bill, etc.), Aadhar card, passport, or voter ID for the owner of the business.
3. Business Registration Proof:
- For Proprietorship: A copy of the PAN card.
- For Partnership Firms: Partnership deed and PAN card.
- For Private/Public Limited Companies: Certificate of incorporation and Memorandum of Association (MOA) or Articles of Association (AOA).
- For LLP: LLP agreement and PAN card.
4. Bank Account Proof:
- A cancelled cheque or bank statement that contains the business name and account details.
5. Photographs:
- Recent passport-size photographs of the business owner(s), directors, or authorized signatories.
6. Authorization Proof:
- For Authorized Signatory: A letter of authorization (if someone other than the business owner is submitting the GST registration application).
7. Other Documents (if applicable):
- For Casual Taxable Person/Non-Resident Taxable Person: Passport and visa details.
- For E-commerce Operators: Business’s details along with the service provider’s authorization.
- For HUF (Hindu Undivided Family): Karta’s PAN and a declaration of the family structure.
These documents need to be uploaded in digital format (usually PDF or JPEG) during the GST registration process. Ensure that all documents are clear, legible, and up-to-date to avoid delays in processing the registration application.
The following categories of businesses and individuals are required to register for GST:
1. Businesses with a Turnover Above the Threshold:
- Regular GST Registration: Businesses whose aggregate turnover exceeds the prescribed threshold limit in a financial year.
- For most states: ₹40 lakhs.
- For special category states: ₹20 lakhs (e.g., Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, North Eastern states).
- For service providers: ₹20 lakhs (₹10 lakhs for special category states).
2. Inter-State Traders:
- Businesses or individuals engaged in the supply of goods or services across states (i.e., inter-state supply) must register for GST, regardless of their turnover.
3. Casual Taxable Persons:
- Individuals or businesses engaged in temporary or occasional taxable supply of goods or services, such as participating in trade fairs, exhibitions, or conducting business temporarily.
4. Non-Resident Taxable Persons:
- Businesses or individuals who do not have a permanent establishment in India but make taxable supplies in India.
5. E-commerce Operators and Aggregators:
- E-commerce platforms that facilitate the supply of goods or services through the platform. These platforms must register under GST to collect tax at source (TCS) on behalf of the suppliers.
6. Businesses Providing Online Information and Database Access or Retrieval (OIDAR) Services:
- Businesses or individuals supplying digital services (like online courses, digital content, etc.) to non-taxable online recipients in India.
7. Agents or Intermediaries:
- Agents or intermediaries who provide services for the supply of goods or services. This includes businesses acting as commission agents, brokers, or facilitators.
8. Businesses Liable to Pay Tax Under Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM):
- Businesses required to pay tax on behalf of their suppliers under the reverse charge mechanism. For example, when goods or services are received from unregistered suppliers.
9. Taxpayers Who Deduct or Collect Tax at Source (TDS/TCS):
- Businesses or individuals who are required to deduct tax at source (TDS) or collect tax at source (TCS), such as government departments or certain e-commerce operators.
The GST tax rate in India is structured into different tax slabs based on the type of goods and services. The rates are categorized as follows:
1. 0% (Exempted)
- Goods: Items of basic necessity like fresh fruits and vegetables, bread, eggs, and certain medicines.
- Services: Health care services, education services, and public transport.
2. 5%
- Goods: Items like life-saving drugs, footwear (under ₹1,000), and certain food items.
- Services: Transport services, including services by metro, railways, and airlines; hotel services (below ₹1,000 per night).
3. 12%
- Goods: Processed food items, soaps, and detergents.
- Services: Services like telecom, business consulting, and restaurants (not under the Composition Scheme).
4. 18%
- Goods: Consumer goods like cosmetics, hair care products, mobile phones, and televisions.
- Services: Restaurant services, construction services, and banking services.
5. 28%
- Goods: Luxury goods such as high-end cars, motorbikes, and tobacco products.
- Services: Hotel services (above ₹7,500 per night), air-conditioned restaurants, and entertainment services.
Special Rates and Cesses:
- Additional Cess: For luxury goods and sin goods (like tobacco and aerated drinks), a cess is applied in addition to the applicable GST rate.
- For example, a cess of 22% is levied on luxury cars in addition to the standard 28% GST.
- Sin goods such as tobacco and pan masala also attract a cess.
The GST Council periodically revises tax rates, so businesses need to stay updated with any changes.
To obtain a GST certificate, follow these steps:
1. Complete the GST Registration Process:
- Visit the GST Portal: Go to the official GST portal at www.gst.gov.in.
- Fill out the GST Registration Form: Submit all necessary details about your business, such as legal name, PAN, business address, bank account information, etc.
- Submit Required Documents: Upload documents like PAN card, proof of business address, proof of identity, etc.
- Verification: After submission, the GST authorities will verify the application and documents.
- Receive Application Reference Number (ARN): After successfully submitting the application, you will receive an ARN that can be used to track the status of your registration.
2. Approval and GSTIN Assignment:
- Verification by Authorities: The GST authorities will verify the details provided in the registration form and the uploaded documents.
- GST Registration Certificate: Once the GST registration is approved, you will receive your GSTIN (GST Identification Number).
- Certificate Generation: The GST registration certificate will be made available on the GST portal.
3. Download the GST Certificate:
- Log in to the GST Portal: Use your credentials to log in to the portal.
- Navigate to Services > Registration > View/Download Certificate: You can find the option to download your GST registration certificate.
- Download and Print: Download the GST certificate (PDF format) and take a printout for your records.
Key Points:
- The GST registration certificate includes the GSTIN and details such as your business name, legal entity, and the effective date of registration.
- Once the registration is approved, the certificate is valid as long as your business remains operational and complies with GST regulations.
The turnover limit for GST registration varies depending on the type of business and the location (general or special category states). The turnover limit refers to the annual aggregate turnover of a business in a financial year, beyond which it is mandatory to register for GST.
1. For Goods Suppliers:
- Normal States: ₹40 lakhs (annual turnover).
- Special Category States (e.g., Jammu & Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, North Eastern States): ₹20 lakhs.
2. For Service Providers:
- Normal States: ₹20 lakhs (annual turnover).
- Special Category States: ₹10 lakhs.
3. For E-commerce Operators:
- Threshold Limit: ₹40 lakhs for goods and ₹20 lakhs for services, applicable to e-commerce operators who are required to collect tax at source (TCS).
4. For Casual and Non-Resident Taxable Persons:
- There is no turnover limit for casual or non-resident taxable persons; they must register regardless of their turnover.
5. For Composition Scheme:
- Businesses opting for the Composition Scheme have a lower turnover limit to qualify:
- Goods Suppliers: ₹1.5 crores (in most states).
- Special Category States: ₹75 lakhs.
Note:
- Voluntary Registration: Even if the turnover is below the prescribed limits, businesses can voluntarily register for GST to avail of benefits like input tax credit (ITC).