CE Certification
Before a product may be sold in the European Union, it must first receive European
Conformity Certification. The CE Certificate indicates that a product has been tested by the
manufacturer and found to comply with EU safety, health, and environmental protection
standards. So, what exactly are you waiting for? Obtain CE certification for your product by
contacting legaltax.in
CE Certification


CE Certification
The term “CE” indicates that the manufacturer or importer complies with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards. It’s important to note that CE is not a quality certification mark. CE marking is mandatory for products sold within the European Economic Area (EEA), but it can also be applied to products sold outside the EEA, as long as they adhere to EEA standards. The CE mark signifies that the product can be sold freely within the EEA, regardless of its country of origin. It typically includes the CE logo and, if applicable, a four-digit code of the certifying body involved in the conformity assessment process. “CE” stands for “Conformité Européenne,” meaning “European Conformity” in French. In essence, the CE marking serves as a passport for a product to be sold in the European market, demonstrating compliance with the essential health and safety requirements of all applicable directives.
Nations That Requires the CE Marking
The CE marking is a legal requirement for certain products intended for sale in the European Union (EU), the European Free Trade Association (EFTA), and Turkey. This applies to both products manufactured within these regions and products imported from other countries, affirming that the goods comply with EU standards. Following Brexit, the UK introduced the UKCA (UK Conformity Assessed) marking as its equivalent conformity indicator, which is mandatory for goods sold in Great Britain. However, CE-marked products can still be used in the UK as of January 1, 2023.
Since Northern Ireland remains aligned with the European Single Market under the Northern Ireland Protocol, the CE mark continues to be a legal requirement for products sold in that region. The UKCA mark can also be used alongside the CE mark, though it is not mandatory. Products for sale in the UK may feature both marks.
As of 2019, CE marking was not mandatory for countries under the Central European Free Trade Agreement (CEFTA). However, some members of CEFTA, such as Serbia, Albania, Montenegro, and North Macedonia, have applied for EU membership, and many of these countries have adopted EU standards in their national laws, similar to former CEFTA members who joined the EU.
Types of Documents Which Are Required to Secure CE Marking
The technical file is a collection of documents that demonstrate a product’s conformity with CE-marking requirements. It should reflect the applicable safety requirements and include information on the design, manufacture, and operation of the product. Additionally, the technical file must be available for inspection by the relevant market surveillance authorities immediately after the product is placed on the market within the European Union. In some cases, the documentation may also need to be submitted to a notified body for review.
Technical documentation typically covers the following aspects:
- Design and manufacturing details
- Safety and performance data
- Risk assessments
- Compliance with relevant standards
The technical documentation can be stored in either electronic or paper format, and it must be retained for up to ten years after the last unit of the product is placed on the market. In most cases, this documentation must remain available within the European Economic Area (EEA).
Procedural Approach to Secure CE Certification in India
Depending on the risk level of the product, CE marking is applied by the manufacturer, who must ensure the product meets CE marking standards. In some cases, if a product carries a low risk, it can be self-certified, which involves the manufacturer making a declaration of conformity and affixing the CE mark.
Self-certification is only applicable to products deemed low-risk, as outlined in the product’s category instructions. To obtain certification, the manufacturer must:
- Verify if the product requires CE marking.
- Ensure the product complies with all applicable requirements.
- Choose the appropriate conformity assessment procedure, based on the product’s risk category and instructions.
There are various conformity assessment modules, but self-certification is typically used for low-risk items. Other processes often require “type approval” and a production conformity assessment by a notified body. Some common modules for the conformity assessment process include:
- Module A: Internal production control.
- Module B: EC type examination.
- Module C: Conformity to type.
- Module D: Production quality assurance.
- Module E: Product quality assurance.
- Module F: Product verification.
- Module G: Unit verification.
- Module H: Full quality assurance.
The severity of the risk is determined by the category of each device. The higher the category, the higher the risk. After specifying the category, the manufacturer must apply the appropriate procedure for securing certification, verifying that the applicable modules for the product category have been implemented. Additionally, the name of the notified body involved in the certification process and the certification number (model) must be provided.
Notified bodies are agencies assigned by a member state, in accordance with the accreditation process, and notified through the European Commission. These bodies act as autonomous inspection agencies and follow the procedures outlined in the applicable modules. Manufacturers can choose any notified body within a member state of the European Union.
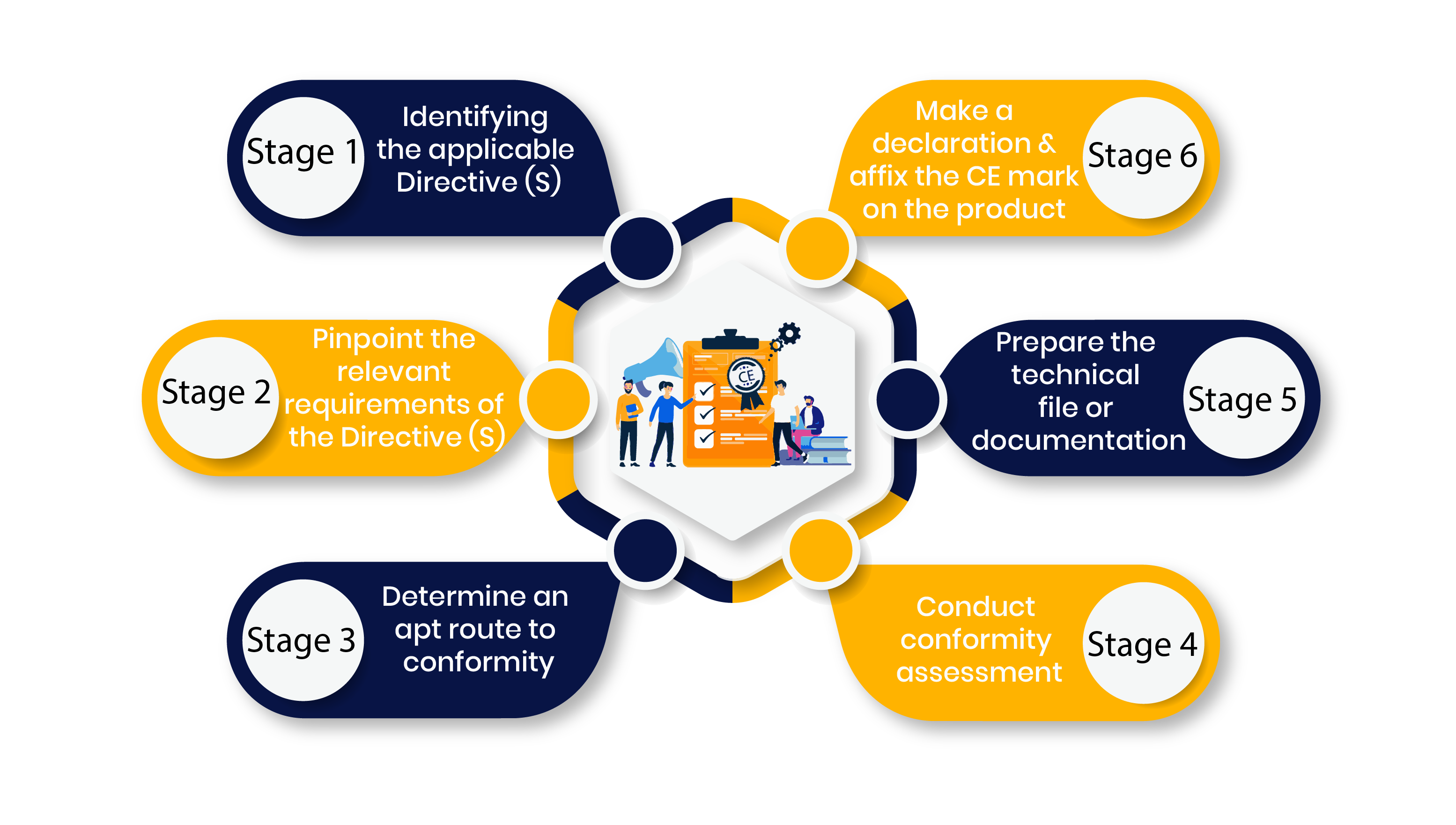
Self-certification involves the following steps:
Stage 1: Identifying the Applicable Directive(s)
The first step is to determine if the product requires CE marking. Only products falling within at least one of the sectoral directives require the CE mark. Currently, over twenty regional directives mandate CE marking, covering products like machines, electrical items, medical devices, pressure equipment, toys, PPE, construction products, and wireless equipment.
To determine which directives apply, the scope of each directive must be read and compared to the product (e.g., “Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU”). If the product doesn’t meet any regional directive, CE marking is not required.
Stage 2: Pinpoint the Relevant Requirements of the Directive(s)
Each directive contains essential requirements the product must meet before it can be sold. The best way to demonstrate compliance with these requirements is to adhere to relevant harmonized standards, though their use is typically voluntary. Harmonized standards can be found in the official journal or the New Approach website launched by EFTA and the European Commission.
Stage 3: Determine an Apt Route to Conformity
In addition to self-declaration, there are several ‘verification routes’ to ensure conformity based on the product’s classification and instructions. Some products, such as fire alarms, invasive medical equipment, pressure equipment, and elevators, require third-party involvement (notified bodies).
Verification routes include:
Product evaluation by the manufacturer The manufacturer evaluates the product and undergoes a mandatory audit of production control by the notified body.
Evaluation by the notified body: This includes EC type testing, with a required production control audit of the factory.
Stage 4: Conduct Conformity Assessment
Once all required items are identified, the product’s conformity to the essential requirements of the directive must be assessed. This may involve testing and conformance assessment according to the harmonized standard(s) indicated in Stage 2.
Stage 5: Prepare the Technical File or Documentation
The technical file is a key requirement for CE marking. It must be prepared in line with EU directives and include details such as product specifications, safety requirements, and manufacturing details.
After completing the conformity assessment, the EU Declaration of Conformity must be completed. This applies to partially completed machinery as well. The Declaration of Conformity should include:
- Manufacturer name and address
- List of products with descriptions and serial numbers
- List of relevant regional directives
- A statement of compliance with applicable requirements
- Name, designation, and signature of the responsible person
- Details of the authorized representative (if applicable)
Finally, the CE mark is affixed to the product once the EU Declaration of Conformity is finalized.
Important Functions Performed by the Notified Body
Conformity assessment provides services to manufacturers of products in areas of public interest. European countries are required to notify conformity assessment bodies within their jurisdiction in accordance with the principles outlined in Decision 768/2008/EC.
Notified Bodies:
-
: Notified Bodies are free to offer their conformity assessment services to operators both inside and outside the EU.
Jurisdiction: Some bodies may perform these services within EU countries or in non-EU countries.
Transparency and Fairness: Notified Bodies must operate in a transparent, non-discriminatory, autonomous, and fair manner.
Qualified Personnel: They must employ qualified personnel to conduct conformity assessments in line with the relevant laws.
Confidentiality: Appropriate measures must be in place to ensure the confidentiality of protected information during the assessment process.
Insurance: Notified Bodies should have suitable insurance to cover their professional activities unless liability is covered under national law.
Reporting: They must provide necessary details to their notification authority, market monitoring agencies, and other notified bodies.
General Traits of CE marking
The CE marking must be clearly and permanently affixed to the product by the manufacturer or its authorized representative in the European Union, following the legal requirements.
When a manufacturer places the CE mark on a product, it signifies that the product complies with all applicable directives and legal requirements. These may include, but are not limited to:
- Low Voltage Directive
- EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) Directive
- ATEX (Explosion Protection) Directive
- Other relevant legal requirements
By affixing the CE mark, the manufacturer assures that all necessary assessments have been completed to ensure conformity with the relevant directives.
The CE marking, as amended by Council Directive 93/68/EEC, is part of several directives, such as:
- Directive 88/378/EEC (Safety of Toys)
- Directive 87/404/EEC (Ordinary Pressure Vessels)
- Directive 89/106/EEC (Construction Products)
- Directive 90/385/EEC (Active Implantable Medical Devices)
- Directive 91/263/EEC (Telecommunication Terminal Equipment)
- Directive 93/42/EEC (Medical Devices)
- Directive 89/392/EEC (Machinery)
- Directive 92/42/EEC (New Hot Water Boilers Powered by Liquid or Gaseous Fuels)
The CE mark should have the initials “CE,” with both letters maintaining the same vertical dimension, not less than 5 mm. If the product does not allow the CE mark to be directly affixed, it should be placed on the packaging or accompanying documents.
In cases where a directive requires the involvement of a third party (such as a notified body) in the conformity assessment process, the identification code of that body should be placed on the reverse of the CE logo.
